Contact dermatitis is a common skin condition that occurs when your skin comes into direct contact with an irritant or allergen. This leads to an itchy, inflamed rash, which can range from mild to severe depending on the cause and your skin’s sensitivity. You can prevent flare-ups and better manage your symptoms by understanding its causes.
Types of Contact Dermatitis
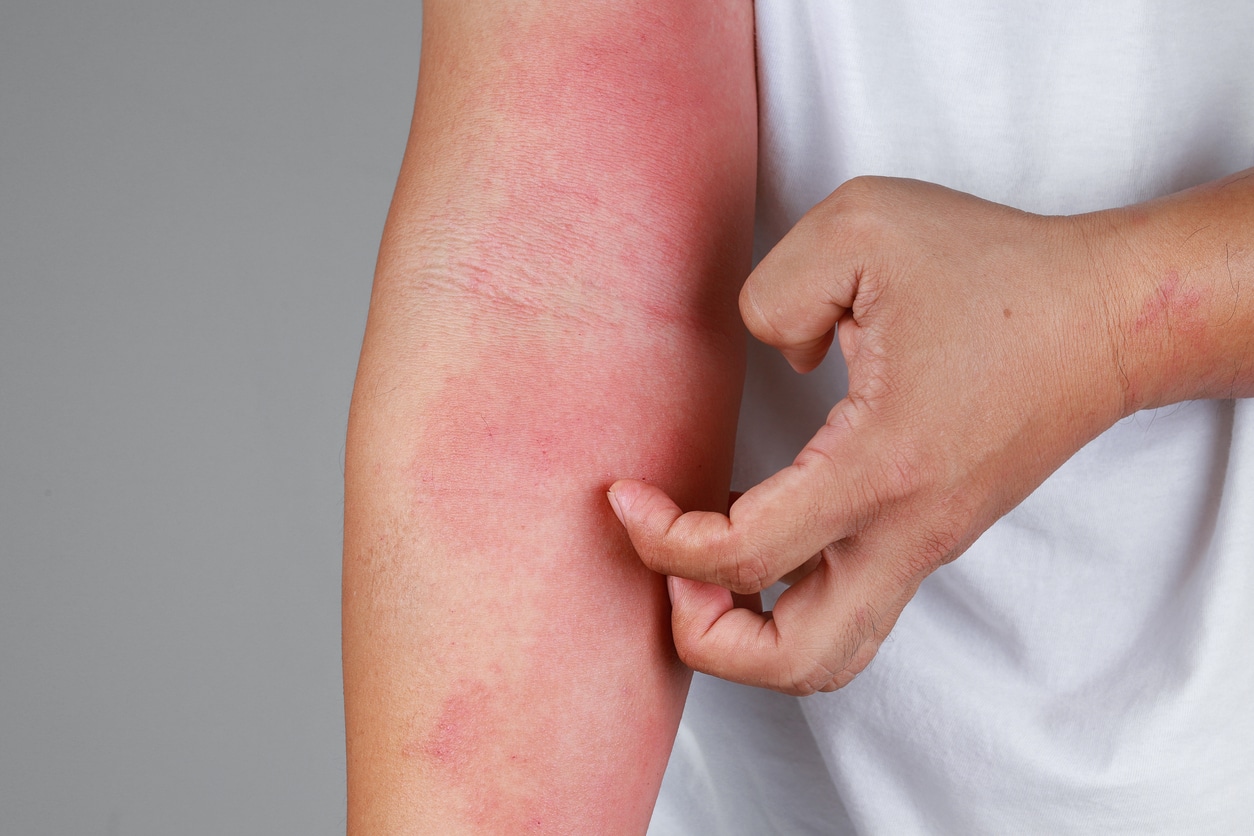
There are two main types of contact dermatitis: irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis.
Irritant contact dermatitis is the more common form and happens when the skin is exposed to substances that cause irritation. These can include harsh soaps, detergents, solvents or even prolonged exposure to water. This type of dermatitis often affects people who work in environments where their skin is frequently exposed to chemicals, such as healthcare workers, hairdressers or cleaners. Symptoms usually develop quickly after contact and can include redness, itching and dry, cracked skin.
Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when your skin reacts to an allergen. Unlike irritant dermatitis, this type develops after repeated exposure to a specific substance that triggers an allergic reaction. Common allergens include nickel, fragrances, latex, and certain plants, such as poison ivy. The reaction may not appear immediately, sometimes taking 24 to 48 hours to show up, and can cause a red, itchy rash, swelling or even blisters in more severe cases.
Allergic contact dermatitis was originally thought to be rare, but data indicates it is a common condition affecting 20% of children.
Managing and Treating Contact Dermatitis
The best way to manage contact dermatitis is by identifying and avoiding the irritant or allergen that triggers the reaction.
For allergic contact dermatitis, it’s crucial to determine the allergen causing the reaction. An allergy test can confirm substances to avoid. Once the allergen is identified, avoiding contact with it is the most effective way to prevent future reactions.
Symptom management typically includes over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams from places like LoRex Drugs to reduce inflammation and itching. In more severe cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger corticosteroids. Oral antihistamines can also help alleviate itching, especially in cases of allergic contact dermatitis. Keeping the affected area clean and applying cool compresses can soothe irritation as well.
If the rash persists for more than a few days, spreads or is accompanied by severe pain or swelling, see a doctor.
By taking preventative measures and using appropriate treatments, you can protect your skin and reduce the impact of contact dermatitis. To learn more about skin allergies or to schedule a test, contact Carolina Pines ENT to schedule a consultation.
